For each HTML element
Iterates over a list of selected elements in an HTML document.
A typical use case for this action is extracting relevant content (or elements) from an HTML document.
Menus, scripts, headers, and footers can be removed so that the result is the 'real' content. The extracted content elements can then be inserted into a vector database, and used for Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) in an AI chat.
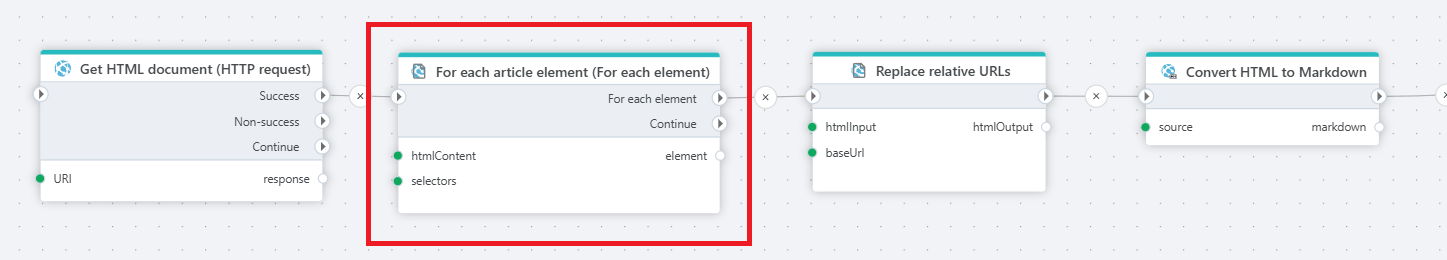
Example 
This Flow retrieves an HTML page, extracts relevant elements using CSS selectors, fixes links in each element, and finally converts it to Markdown text.
Properties
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Title | Optional | The title of the action. |
| HTML content | Required | The source HTML document to parse. This can be a string, a byte array, or a Stream. |
| CSS selectors | Required | CSS selectors are the query expressions to identify elements for extraction. See below for details and examples. |
| Return variable name | Optional | Name of the variable containing the current element. |
| Description | Optional | Additional notes or comments about the action or configuration. |
Returns
Each element is returned as a string.
CSS Selectors
Selectors can include HTML tags, attributes, class names, or css elements. Multiple expressions are separated with commas.
Click here for a full reference on CSS Selectors
For example, given the following HTML:
<html>
<header>test</header>
<body>
<div>
<div class="x">test1</div>
<div class="x">test2</div>
</div>
To extract the div's using class='x', we can use the CSS selector 'div.x'.
This returns 2 elements:
<div class="x">test1</div>
<div class="x">test2</div>
To also include the header, we can use the selector 'header, div.x'.
This returns 3 elements:
<header>test</header>
<div class="x">test1</div>
<div class="x">test2</div>