Auto transactions
Auto Transactions enables defining of one or more transactions that should be derived from a source transaction or entity.
A typical use case for using Auto Transactions is when working with driver based (financial) models. Business drivers, such as Human Resources, almost always comprise sub items such as salary, health insurance, retirement plans, life insurance and so more. By using Auto Transactions, you can establish a "master-details" relationship between an entity and its sub-items. This allows for automatic generation of sub-items into your budget, forecast, or any other dataset, eliminating the need for manual entry at a granular level.
Properties
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Key columns | Optional | All Auto Transaction tables must have at least one logical key. If no Primary Key is defined on the table in InVision, or you want to use a different set of columns to make up the key, you can specify the key manually here. Flow uses the key to find which Auto Transactions rows to return from the FilterByContext() or FilterByContextDistinctByTypeField() methods. |
| Data | Optional | Specifies the fields / columns from the Auto Transaction table that you want to use for business logic. By default, all non-key columns are automatically available. |
| Key mappings | Optional | Use this option to define explicit mapping between the Key columns and the (corresponding) columns in the data source when names does not match. Flow determines which Auto Transactions to use by comparing the values in the Key columns to the corresponding columns in the input row from the data source. If not specified otherwise, it matches against columns with the same name. If you need a different behavior, you need to specify the mapping between the keys explicitly. |
| Auto Transaction type | Optional | Specifies the name of the column that defines the Auto Transaction type. You can consider Auto Transaction type as a way to categorize Auto Transactions. For example "Company car" may be a type in the "Employee benefits" Auto Transactions table. |
| Options | Optional | Disable caching: Enable this option if you are generating the data in the Auto Transaction table using a custom SQL script. When generating data into a table using a custom SQL script, InVision will not be able to detect the change and notify Flow to invalidate its cache. You can also use the Remove InVision object from cache action to programatically evict the table from cache. |
Using Auto Transactions to produce calculated rows
To use Auto Transactions to produce calculated rows, create a Flow and add the following actions
- Define Auto Transactions to use
- Add a Calculation Flow db output action
- Add a Calculation Flow db input action
- Add a Function action and call
AutoTransactions.UseContext(...)(see example below). - Add a Function action and implement the calculations (see example below).
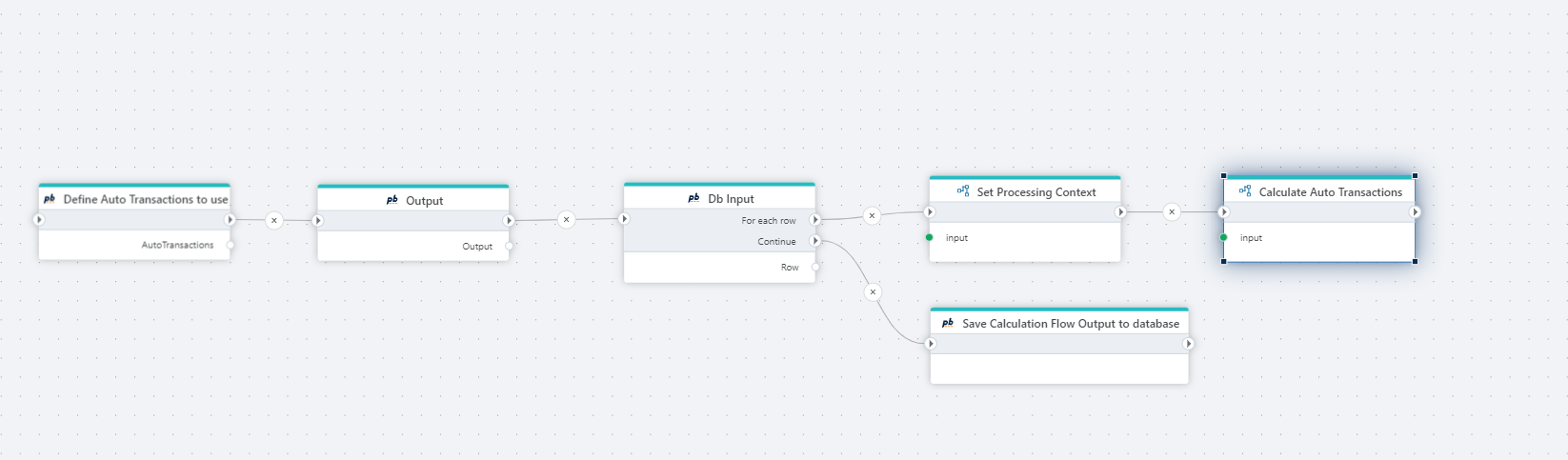
Set processing context
From step 4) above, we need to set the context on the Auto Transactions search index so that when we call FilterByContext() or FilterByContextDistinctByTypeField(), we get back the Auto Transaction definitions that should be used to generate the Auto Transactions for the current context (for example department, employee or account).
private void SetProcessingContext(MyWorkspace.ForecastInput input)
{
this.AutoTransactions.UseContext(input);
}
Calculate Auto Transactions
private void Calculate(MyWorkspace.ForecastInput input)
{
// Returns which employee benefits to generate for the given context.
foreach(var autoTrans in this.AutoTransactions.EmployeeBenefits.FilterByContextDistinctByTypeField())
{
this.Output.Add(AccountID: autoTrans.TargetAccountID, Amount: input.Amount * autoTrans.Factor);
}
}
API
Properties
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| DecayFactor | Used to calculate the match score for each Auto Transaction row returned by FilterByContext() or FilterByContextDistinctByTypeField(). The default value is 0.5. The topic about Set lookups explains how match score is computed. |
Methods
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| FilterByContext() | Returns the Auto Transactions having keys matching the key of the data source input row currently used as context. |
| FilterByContextDistinctByTypeField(l) | Returns the Auto Transactions having keys matching the key of the data source input row currently used as context, in addition to also filtering by the Auto Transaction type property. If you have specified the Auto transaction type property, you must use this API to avoid the possibility of getting multiple matches pr Auto Transaction type. |
| UseContext(input) | |
| Set{FieldId}Context(string) | Sets the value used for matching against {FieldId} in the Auto Transaction table. For example, SetDepartmentIDContext("a") will set "a" as the value to match against the DepartmentID field in the Auto Transaction table. Use the Get{FieldId}Context() and Set{FieldId}Context() when you need to change the search context on a granular level, for example if you generate Auto Transactions in a Distribution Key loop. |
| Get{FieldId}Context() | Gets the value value used for matching against {FieldId} in the Auto Transactions table. For example GetDepartmentIDContext() returns the department id that is used for matching against the DepartmentID field in the Auto Transaction table. |