Filtering table data
You can enable filtering for individual tables by defining your table queries with a parameterized WHERE clause. This allows filter values set in the workbook to dynamically update the query results.
To apply filters, use the Execute Expression action available for the Table Explorer component in the Workbook Designer. In the event handler that reacts to filter changes, use the SetParamValue() function to assign a value to the query parameter.
- Use Execute Expression available for the Table Explorer
- Set the SQL filter parameter value using
SetParamValue()function - Call the
Refresh()method
Add a filter to the workbook page
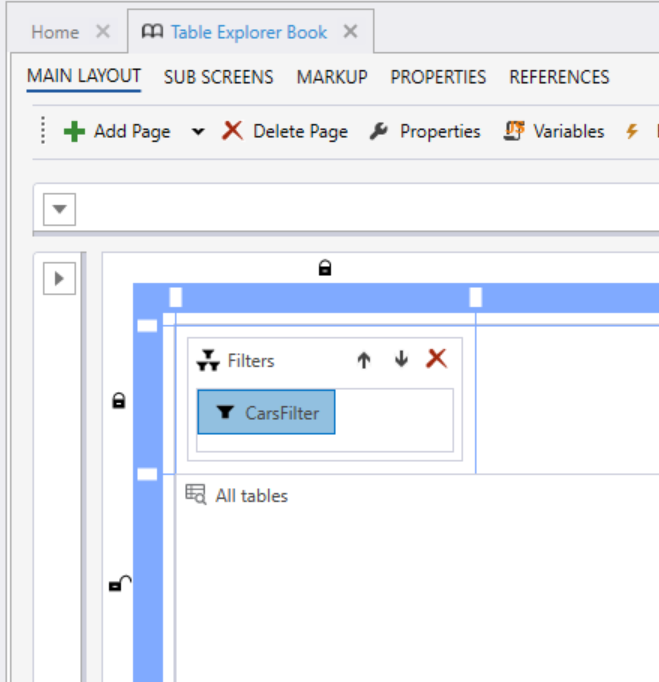
Set an event for the filter change action
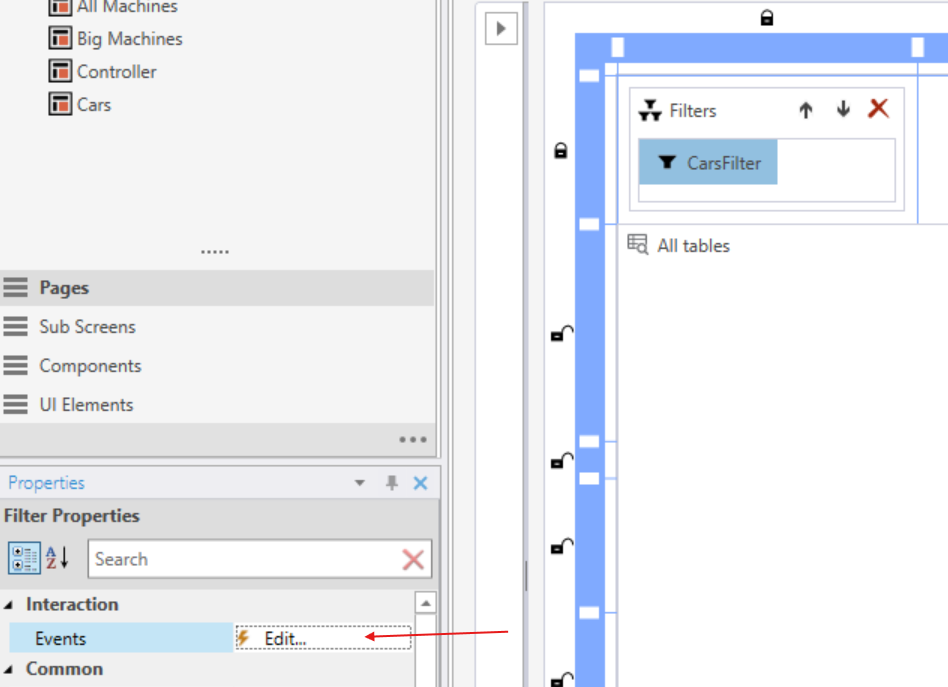
Configure the filter change event
Use the Execute Expression action for the Table Explorer and configure instructions to:
- Set the SQL parameter value (e.g., based on the selected filter item).
- Call
Refresh()to reload the table data with the updated parameter value.
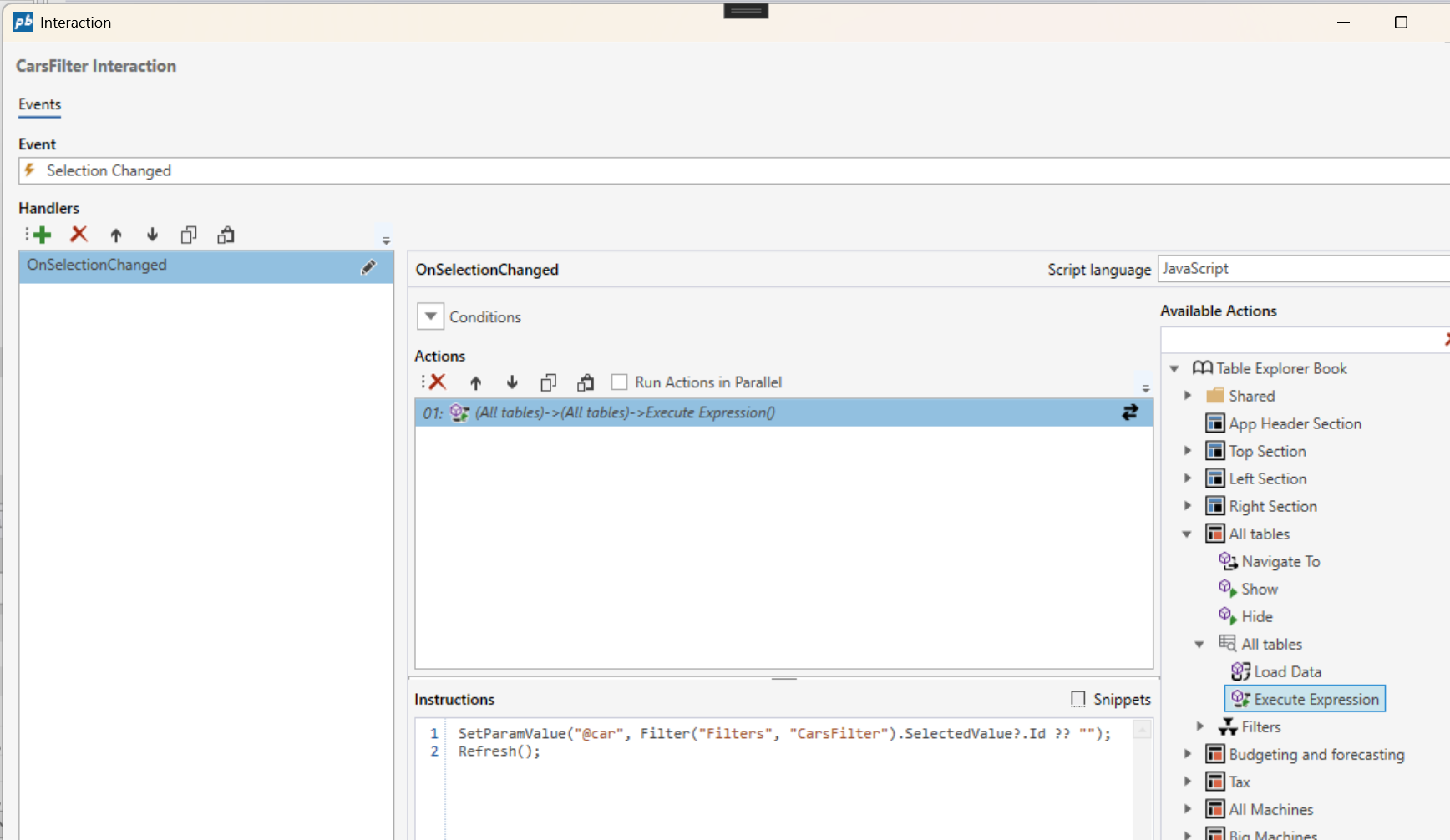
Example
The following example shows how to set the SQL parameter @car based on the selected value in a filter named CarsFilter, followed by calling the refresh method:
SetParamValue("@car", Filter("Filters", "CarsFilter").SelectedValue?.Id ?? "");
Refresh();
Example
This example shows how the sql parameter @car is used in the query WHERE clause:
SELECT tx.[Name],tx.[Id]
FROM [dbo].[Setting_Cars_2fd73_05062025050634667] tx
WHERE tx.[Name] = @car
Extended filtering table data, with multiple filters and values
You can filter the individual tables with multiple values and multiple filters by defining your table queries with parameterized WHERE clause and JOIN filters, and defining your filters at the top of the query. This allows filter values set in the workbook to dynamically update the query results.
To apply filters with multiple values, use the Execute Expression action available for the Table Explorer component in the Workbook Designer. In the event handler that reacts to filter changes, use the SetFilter() function to assign a values to the query parameter.
- Use Execute Expression available for the Table Explorer
- Set the SQL filter parameter value(s) using
SetFilter()function
SetFilter(filerName: string, Filter("Filters", filterName: string).SelectedValues);
- Call the
Refresh()method
Add filter(s) to the workbook page and set event(s) for filter change action(s) (for each filter if applicable)
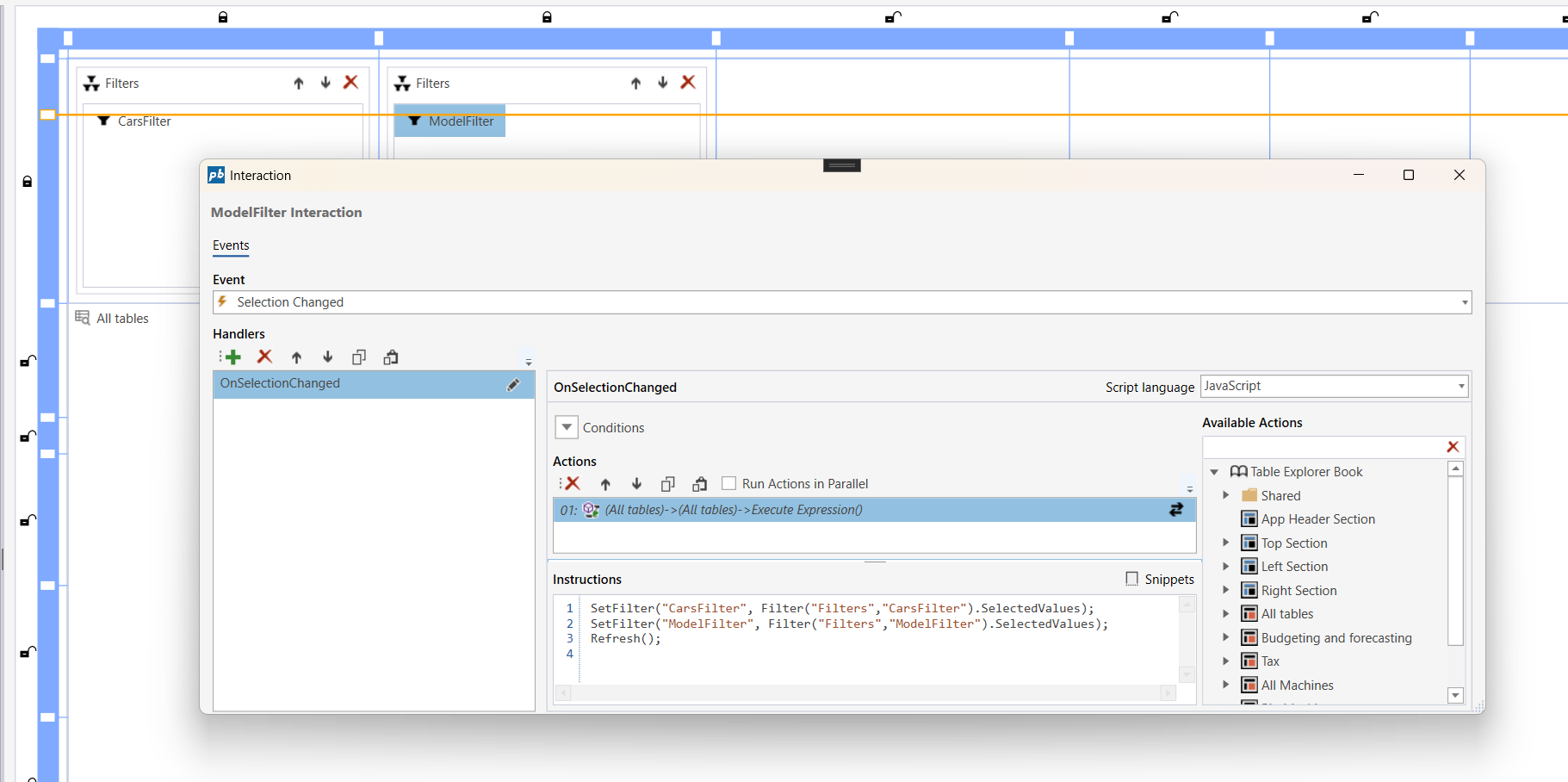
Configure the filter change event
Use the Execute Expression action for the Table Explorer and configure instructions to:
- Use the
SetFilter()function. - Call
Refresh()to reload the table data with the updated filters and values.
Example
The following example shows how to set the SQL filters for cars based on the selected values in a filter named CarsFilter, and the models based on the selected values in a filter named ModelFilter followed by calling the Refresh() method:
SetFilter("CarsFilter", Filter("Filters", "CarsFilter").SelectedValues);
SetFilter("ModelFilter", Filter("Filters", "ModelFilter").SelectedValues);
Refresh();
The Table Explorer will then filter the selected table(s) with the filters, given that the tables load queries have the filters declared and joined.
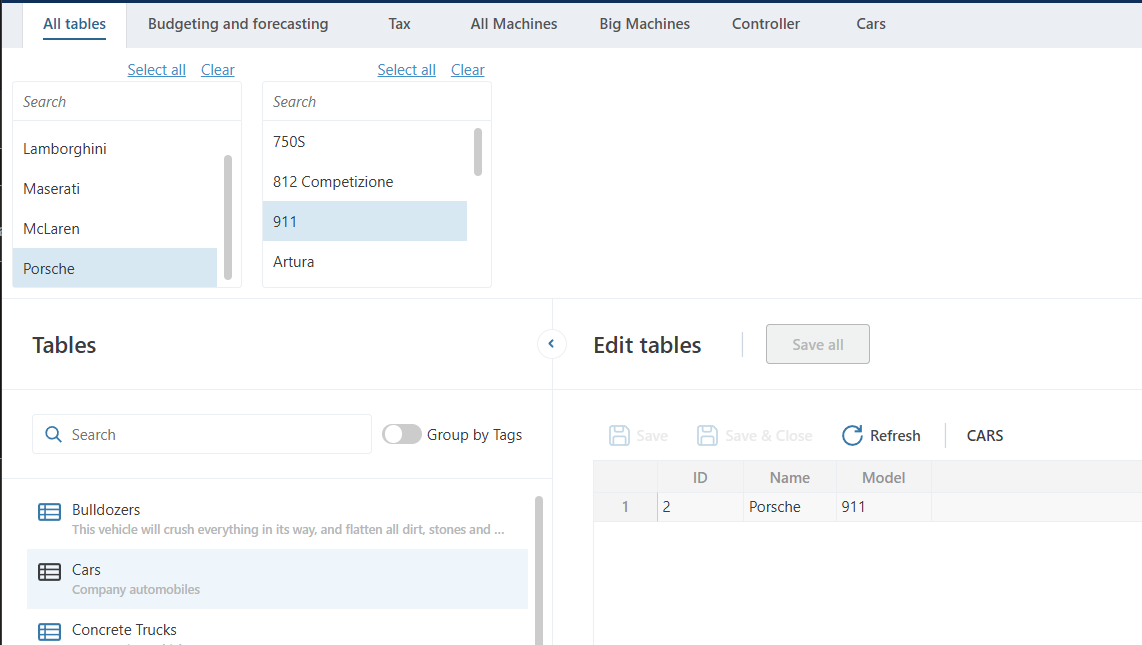
Example
This example shows how the filters are applied in the sql:
@Declare_FilterAlias(CarsFilter, CF)
@Declare_FilterAlias(ModelFilter, MF)
SELECT DISTINCT tx.[Name],tx.[Id],tx.[Model]
FROM [dbo].[Setting_Cars_2fd73_05062025050634667] tx
JOIN @Object_Name(CF) cf ON tx.[Name] = cf.[Name]
JOIN @Object_Name(MF) mf ON tx.[Model] = mf.[Model]
WHERE @Values_Equal(CF)
AND @Values_Equal(MF)