Bad data
When importing data from a CSV format, you often get bad data in form of badly formatted values, missing fields, or simply unexpected values. In a large data set, bad data is often hard to track down. By enabling Error handling behaviors in the Data import options, you can record the bad data encountered during a CSV import and investigate which rows and fields are causing the import to fail.
Bad data is stored in the BadData property of the action, and can be read as an IEnumerable<BadDataRecord> or as an IDataReader. This makes it easy to dump the information to a database table or a file for debugging purposes.
The BadDataRecord object has the following properties:
| Name | Data type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| RecordIndex | Int32 | The index of the record / row in the CSV data set. |
| RecordData | String | The raw record / row in the CSV data set. |
| DebugInfo | String | Descriptive information about what caused the data to fail validation. |
Example - Dump bad data to SQL Server
To dump bad data to a SQL Server table, do the following:
- Create a table with the following schema (You can name it whatever you like).
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[BadData](
[RecordIndex] [int] NULL,
[RecordData] [nvarchar](max) NULL, -- Choose a text data type that fits the size of a row from your CSV file
[DebugInfo] [nvarchar](max) NULL -- This field may contain the row data in addition to debugging information, so choose a data type accordingly
) ON [PRIMARY] TEXTIMAGE_ON [PRIMARY]
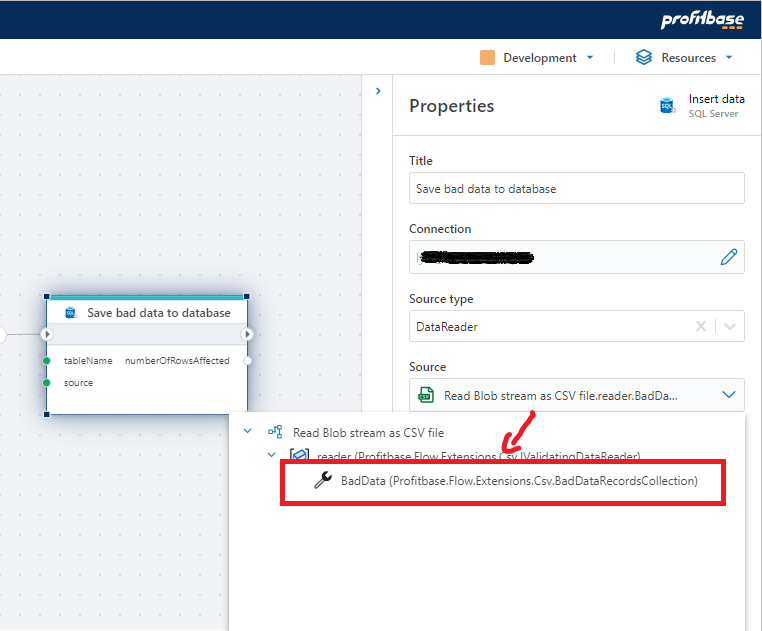
- Add an Insert data action to the Flow after the CSV reader action and connect them.
- Select the
Insert dataaction, and in theproperty panel, choose the BadData collection from the CSV action as theSourceproperty. - In the
Destination tableproperty, specify the name of the table you created in step 1) above ("BadData").